KA for acrylsyre er 0,000056 Beregn pH på 0,10 m vandig opløsning acalculate procent dissociation syre?
1. Opret et isbord
Acrylsyre (ch₂ =chcooh) er en svag syre, så den er kun delvist ioniseret i vand. Vi kan repræsentere dens ionisering med følgende ligevægt:
Ch₂ =chcooh (aq) ⇌ h⁺ (aq) + ch₂ =chcoo⁻ (aq)
| | Ch₂ =chcooh | H⁺ | Ch₂ =chcoo⁻ |
| ------------- | -------------- | ------- | ------------- |
| Indledende (i) | 0,10 m | 0 | 0 |
| Ændring (c) | -x | +x | +x |
| Ligevægt (E) | 0,10 - x | X | X |
2. Skriv KA -udtrykket
Ka =[H⁺] [CH₂ =CHCOO⁻] / [CH₂ =CHCOOH]
3. Erstatte og løse for x
0,000056 =(x) (x) / (0,10 - x)
Da KA er lille, kan vi antage, at X er meget mindre end 0,10, så vi kan forenkle ligningen:
0,000056 ≈ (x) (x) / 0,10
X² ≈ 0,0000056
x ≈ √0.0000056 ≈ 0,00237 m
4. Beregn pH
ph =-log [h⁺] =-log (0,00237) ≈ 2,63
5. Beregn den procentvise dissociation
Procent dissociation =([h⁺] / [initial syre]) * 100%
Procent dissociation =(0,00237 / 0,10) * 100% ≈ 2,37%
Derfor:
* PH på en 0,10 m vandig opløsning af acrylsyre er cirka 2,63 .
* Den procentvise dissociation af acrylsyre i denne opløsning er cirka 2,37% .
 Varme artikler
Varme artikler
-
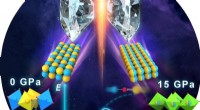 Nye materialer af perovskit udfordrer traditionelle forestillinger om højtrykskemiKemisk intuition fortæller os, at tryk har en tendens til at øge antallet af koordinering, og derfor normalt laver en struktur ordnet, der især gælder for perovskit-lignende forbindelser. Imidlertid,
Nye materialer af perovskit udfordrer traditionelle forestillinger om højtrykskemiKemisk intuition fortæller os, at tryk har en tendens til at øge antallet af koordinering, og derfor normalt laver en struktur ordnet, der især gælder for perovskit-lignende forbindelser. Imidlertid, -
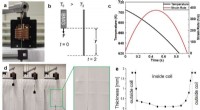 Ved at tilføje belastning, forskere forbedrer metallisk glasFig. 1:Eksperimentel realisering af exciteret væskekøling. Kredit: Kommunikationsmaterialer (2021). DOI:10.1038/s43246-021-00127-0 Metalliske glas - materialer med metalstyrke, men formbare som p
Ved at tilføje belastning, forskere forbedrer metallisk glasFig. 1:Eksperimentel realisering af exciteret væskekøling. Kredit: Kommunikationsmaterialer (2021). DOI:10.1038/s43246-021-00127-0 Metalliske glas - materialer med metalstyrke, men formbare som p -
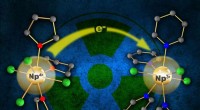 Åbner adgang til at udforske neptuniums syntetiske kemiEn ny, let fremstillet udgangsmateriale (til venstre) indeholdende neptunium (Np3+) kan let fremstilles ved en elektron (e-) overførsel til en moder neptunium (Np4+) forbindelse (højre). Denne proces
Åbner adgang til at udforske neptuniums syntetiske kemiEn ny, let fremstillet udgangsmateriale (til venstre) indeholdende neptunium (Np3+) kan let fremstilles ved en elektron (e-) overførsel til en moder neptunium (Np4+) forbindelse (højre). Denne proces -
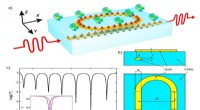 Blod og sved:Bærbare medicinske sensorer vil få et stort følsomhedsforøgelseBiosensor layout (en, c). Bølgelederen er inde i det dielektriske substrat. Resonatoren, realiseret som en ringbølgeleder, er placeret ved grænsefladen mellem det dielektriske materiale og den biologi
Blod og sved:Bærbare medicinske sensorer vil få et stort følsomhedsforøgelseBiosensor layout (en, c). Bølgelederen er inde i det dielektriske substrat. Resonatoren, realiseret som en ringbølgeleder, er placeret ved grænsefladen mellem det dielektriske materiale og den biologi
- Hvad forårsager friktion mellem 2 overflader, der er i kontakt med hinanden?
- Forskere skaber ny nanostruktur, der absorberer bredt spektrum af lys fra alle vinkler
- Tropisk cyklon Joyce gennemblødt nordvestlige Australiens kyst
- Hvordan usikkerhed påvirker livet for alle i Nigerdeltaet
- Har du zink? Ny zinkforskning tyder på nye terapeutiske mål
- Vil du dykke i troperne? Spis ikke revfiskene!