What is a metallomagnet?
Here's a breakdown:
* Traditional Magnets: These magnets use ferromagnetic materials that exhibit strong magnetic properties due to the alignment of their atomic spins. Examples include permanent magnets and electromagnets.
* Metallomagnets: These magnets utilize metallic materials with specific properties, like high electrical conductivity , high spin polarization , and strong exchange interactions . These properties enable them to exhibit magnetic behavior, even if they are not traditionally ferromagnetic.
Examples of metallomagnets include:
* superledende magneter: These utilize superconductors, materials that exhibit zero electrical resistance at low temperatures, to generate extremely strong magnetic fields.
* Organic magnets: Some organic molecules can exhibit magnetic properties due to the presence of unpaired electrons. These molecules can be incorporated into metallic structures to create metallomagnets.
* Spintronic devices: These devices utilize the spin of electrons to store and process information. Metallomagnets play a key role in these devices, enabling the manipulation of electron spins.
Advantages of Metallomagnets:
* High magnetic fields: Metallomagnets kan generere stærkere magnetiske felter sammenlignet med traditionelle magneter.
* Forbedret effektivitet: They can offer better energy efficiency in applications like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and particle accelerators.
* Enhanced control: They allow for better control over magnetic fields, enabling the development of more sophisticated magnetic devices.
Challenges of Metallomagnets:
* Limited availability: Mange metallomagnets kræver specialiserede materialer og fremstillingsteknikker, som kan begrænse deres tilgængelighed.
* Temperature sensitivity: Some metallomagnets exhibit strong temperature dependence, limiting their applications in certain environments.
In summary, metallomagnets are a promising new class of magnets that exploit the magnetic properties of metallic materials. They offer significant advantages over traditional magnets, but they also face some challenges in terms of availability and temperature sensitivity. As research and development continue, metallomagnets are expected to play a key role in various applications, including electronics, medicine, and energy.
Sidste artikelEr Mitten en flydende fast stof eller gas?
Næste artikelNår der forekommer en fysisk ændringer, dannes nyt stof?
 Varme artikler
Varme artikler
-
 Forskere udvikler 3-D printsubstrat med dynamiske bindinger til justerbare egenskaber4-D-print:En farve- og formskiftende blomst i mikrostørrelse skabt ved direkte laserskrivning. Kredit:TU/e Fantastiske former kan laves ved hjælp af 3-D print, men til mange applikationer skal det
Forskere udvikler 3-D printsubstrat med dynamiske bindinger til justerbare egenskaber4-D-print:En farve- og formskiftende blomst i mikrostørrelse skabt ved direkte laserskrivning. Kredit:TU/e Fantastiske former kan laves ved hjælp af 3-D print, men til mange applikationer skal det -
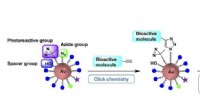 Let monterede guld nanopartikel stilladser tjener som molekylær sondeEt-trins forberedelse af fotoaffinitetsprober ved hjælp af klikbare guld-nanopartikel-prækursorer muliggør hensigtsmæssige målidentifikationsundersøgelser Kredit:Figur modificeret fra organisk og biom
Let monterede guld nanopartikel stilladser tjener som molekylær sondeEt-trins forberedelse af fotoaffinitetsprober ved hjælp af klikbare guld-nanopartikel-prækursorer muliggør hensigtsmæssige målidentifikationsundersøgelser Kredit:Figur modificeret fra organisk og biom -
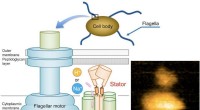 Forskere beskriver mekanismen bag flagellar motilitetFig. 1. Skematisk diagram af den bakterielle flagelmotor og et typisk AFM-billede af oprenset MotPS-kompleks. Kredit:Osaka University Bakterier svømmer på mange forskellige måder, og motorerne, de
Forskere beskriver mekanismen bag flagellar motilitetFig. 1. Skematisk diagram af den bakterielle flagelmotor og et typisk AFM-billede af oprenset MotPS-kompleks. Kredit:Osaka University Bakterier svømmer på mange forskellige måder, og motorerne, de -
 Brug af kvanteprikker og en smartphone til at finde dræberbakterierForskerne Anwar Sunna (til højre) og Vinoth Kumar Rajendran med deres smartphone-aktiverede MRSA-detektor. Kredit:Sunna Lab En kombination af quantum dot nanoteknologi og et smartphonekamera kan s
Brug af kvanteprikker og en smartphone til at finde dræberbakterierForskerne Anwar Sunna (til højre) og Vinoth Kumar Rajendran med deres smartphone-aktiverede MRSA-detektor. Kredit:Sunna Lab En kombination af quantum dot nanoteknologi og et smartphonekamera kan s