Aldrende amerikanske dæmninger udgør en risiko for tusindvis
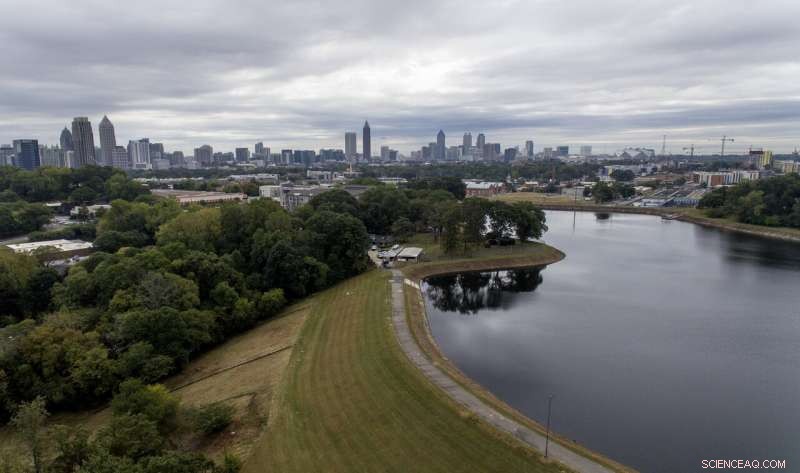

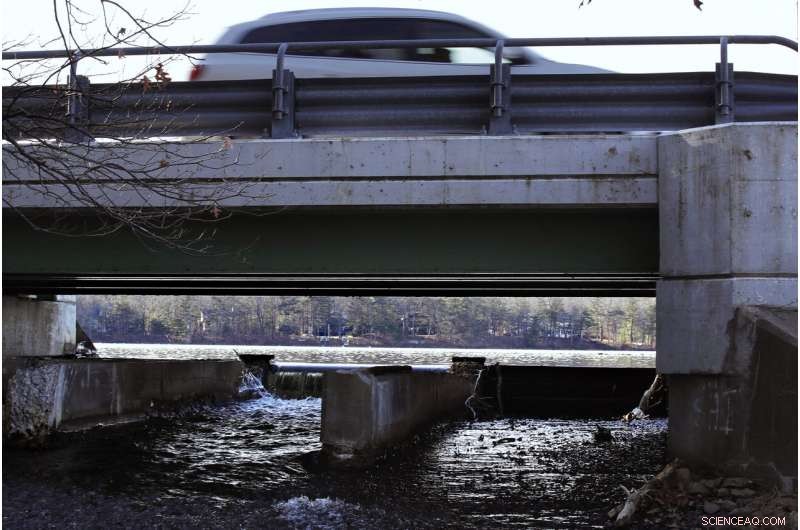
Reservoar nr. 1, en 180 millioner gallon vandforsyning, der har været ude af drift store dele af de sidste par årtier, sidder på baggrund af byens skyline, 15. okt. 2019, i Atlanta. Byen foretog reparationer og bragte den online igen i 2017, kun for at lukke den ned igen, efter at der blev bemærket vandlækager i nærheden af virksomheder placeret under dæmningen. Skulle dæmningen katastrofalt fejle, vandet kan oversvømme mere end 1, 000 enfamiliehuse, snesevis af virksomheder, en jernbane og en del af Interstate 75, ifølge en nødhandlingsplan. (AP Photo/David Goldman)
På en kold morgen i marts sidste år, Kenny Angel fik et hektisk bank på sin dør. To arbejdere fra et forsyningsselskab i det nordlige Nebraska var kommet med en skarp advarsel:Kom ud af dit hus.
Lidt over en kvart mil opstrøms, den 92-årige Spencer Dam anstrengte sig for at begrænse den hævede, isdækkede Niobrara-floden efter en usædvanlig intens sne- og regnbyge. Arbejderne havde forsøgt, men formåede ikke at tvinge dæmningens frosne træporte op. Så, frygter det værste, de flygtede i deres lastbil, stopper for at advare Angel, før han kører væk uden ham.
Minutter senere, dæmningen styrtede ned, at udløse en bølge af vand, der bærer isstykker på størrelse med biler. Angels hjem blev udslettet; hans lig blev aldrig fundet.
"Han havde cirka 5 minutters varsel, uden forudgående varsel dagen før, "Scott Angel, en af Kennys brødre, sagde.
Statsinspektører havde givet dæmningen en "fair" vurdering mindre end et år tidligere. Indtil det mislykkedes, det så lidt anderledes ud end tusindvis af andre i hele USA - og det kunne være et problem.
En mere end to-årig undersøgelse foretaget af The Associated Press har fundet snesevis af dæmninger landsdækkende i endnu værre tilstand, og på lige så farlige steder. De rager over husene, virksomheder, motorveje eller hele samfund, der kan blive udsat for livstruende oversvømmelser, hvis dæmningerne ikke holder.

Denne kombination af billeder leveret af Nebraska Department of Natural Resources, viser Spencer Dam nær Spencer, Neb., i november 2013, top, da den holdt vandet tilbage på Niobrara-floden og igen i marts 2019, efter at dæmningen svigtede under en oversvømmelse. Statsinspektører havde givet dæmningen en "fair" vurdering mindre end et år tidligere. Indtil det mislykkedes, det så lidt anderledes ud fra tusinder af andre i hele USA, og det kan være et problem. (Nebraska Department of Natural Resources via AP)
En gennemgang af føderale data og rapporter indhentet i henhold til statens love om åbne registre identificeret 1, 688 højrisikodæmninger vurderet i dårlig eller utilfredsstillende tilstand sidste år i 44 stater og Puerto Rico. Det faktiske antal er næsten helt sikkert højere:Nogle stater afviste at give tilstandsvurderinger for deres dæmninger, krav om undtagelser fra anmodninger om offentlige registre. Andre har simpelthen ikke vurderet alle deres dæmninger på grund af manglende finansiering, bemanding eller bemyndigelse til at gøre det.
Dødsfald fra dæmningsfejl er faldet, siden en række katastrofale sammenbrud i 1970'erne fik de føderale og delstatsregeringer til at optrappe deres sikkerhedsindsats. Alligevel omkring 1, 000 dæmninger har svigtet i løbet af de sidste fire årtier, dræbte 34 mennesker, ifølge Stanford University's National Performance of Dams Program.
Bygget til oversvømmelseskontrol, vanding, vandforsyning, vandkraft, rekreation eller opbevaring af industriaffald, nationens dæmninger er i gennemsnit over et halvt århundrede gamle. Nogle er ikke længere tilstrækkelige til at håndtere den intense nedbør og oversvømmelser i et skiftende klima. Alligevel bliver de afhængige af at beskytte flere og flere mennesker, efterhånden som boligbyggerier dukker op i nærheden.
"Der er tusindvis af mennesker i dette land, der lever nedstrøms fra dæmninger, der sandsynligvis anses for at være mangelfulde givet de nuværende sikkerhedsstandarder, " sagde Mark Ogden, en tidligere Ohio-dæmningssikkerhedsofficer, som nu er teknisk specialist hos Association of State Dam Safety Officials.
Foreningen vurderer, at det vil tage mere end 70 milliarder dollars at reparere og modernisere landets mere end 90, 000 dæmninger. Men i modsætning til meget anden infrastruktur, de fleste amerikanske dæmninger er privatejede. Det gør det vanskeligt for regulatorer at kræve forbedringer fra operatører, der ikke er i stand til eller villige til at betale de høje omkostninger.
"De fleste mennesker har ingen anelse om sårbarhederne, når de bor nedstrøms fra disse private dæmninger, " sagde Craig Fugate, en tidligere administrator ved Federal Emergency Management Agency. "Når de fejler, de fejler ikke med advarsel. De fejler bare, og pludselig kan du finde dig selv i en situation, hvor du har en mur af vand og snavs, der løber mod dit hus med meget kort tid, hvis nogen, At komme ud."
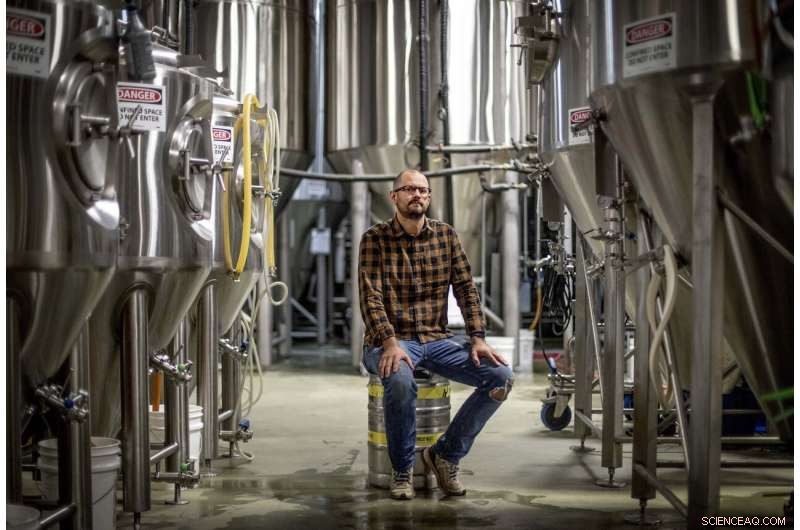

Joel Iverson, driftschef for Monday Night Brewing, er fotograferet i bryggeriet, der ligger ved siden af Reservoir nr. 1, en 180 millioner gallon vandforsyning, der har været ude af drift store dele af de sidste par årtier, 15. okt. 2019, i Atlanta. Iverson har tidligere bemærket, at vand drypper ud af bjergsiden af dæmningen nær det bryggeri, han var med til at grundlægge. "Hvis den går, det kommer til at skylle os væk og en masse øl, " sagde Iverson. (AP Photo/David Goldman)
___
Det er uklart, om Angel, en 71-årig veteran fra Vietnamkrigen, afviste at flygte eller løb simpelthen tør for tid, efter at arbejdere i Nebraska Public Power District advarede ham om, at vandet var ved at vælte over dæmningen nær Spencer, en by med færre end 500 indbyggere.
En advokat for Angels kone, som ikke var hjemme, da dæmningen brød, har anlagt en retssag på $5 millioner med påstand om uagtsomhed. Det hævder, at elforsyningen ikke formåede at vedligeholde dæmningen ordentligt, træne sine medarbejdere eller informere englene om farlige forhold.
Selvom englenes hjem var lige i vejen, dæmningen blev vurderet som en "betydelig" snarere end "høj" fare, hvilket betyder, at det ikke var påkrævet i henhold til Nebraska-loven at have en formel nødhandlingsplan. Omkring 20 % af de statsregulerede højrisikodæmninger på landsplan mangler stadig nødplaner, ifølge U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, som vedligeholder den nationale dæmningsopgørelse.
Ved sidste inspektion i april 2018, Spencer Dams "fair" vurdering blev ledsaget af en ildevarslende notation:"Der findes mangler, som kan føre til dæmningsfejl under sjældne, ekstreme stormhændelser."
Tim Gokie, chefingeniør for Nebraskas dæmningsprogram, sagde, at advarslen skyldtes tidligere vandudsivning, som strømforsyningen rettede ved at installere et afløbssystem. Ultimativt, Gokie sagde, den stigende Niobrara-flod overvældede simpelthen beton- og jorddæmningen, som blev bygget i 1927 for at generere vandkraft, ikke til oversvømmelseskontrol.
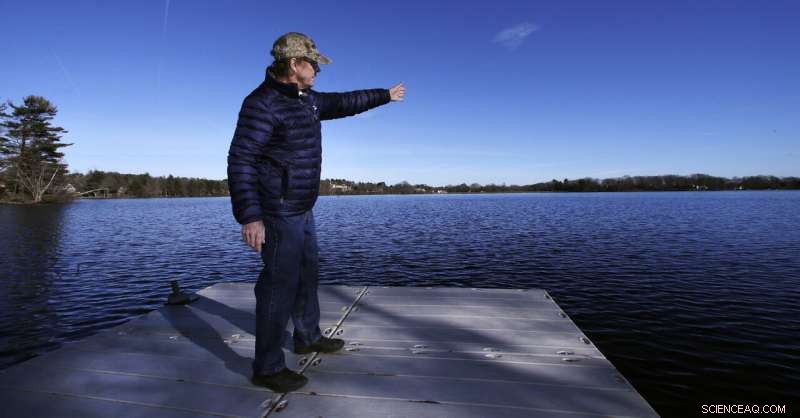

I denne 27. dec. 2018, Foto, Murray Beach, en investeringsbankmand, der bor på bredden af Willett Pond, peger på søens udløb, som ligger på grænsen mellem Norwood og Walpole, Mass. Udslippet ved den 107 år gamle Willett Pond Dam er i stand til at håndtere kun 13 % af vandstrømmen fra en alvorlig oversvømmelse, før dæmningen er overtoppet, ifølge en nylig statsinspektionsrapport. "Vi taler ikke om bare at oversvømme nogens hus. Vi taler om at dække deres hus, " sagde Beach, som tilhører en borgergruppe, der i årevis har drevet lobbyvirksomhed for, at overløbet skal repareres. (AP Photo/Charles Krupa)
"Faktum var, at det bare var en hidtil uset situation, "Nebraska Public Power District talsmand Mark Becker sagde. "Det var ud over, hvad alle havde forventet."
Nebraska var blandt de stater, der var hårdest ramt af storme og oversvømmelser i år, der har forårsaget skader på veje for anslået 1,5 milliarder dollars. dæmninger, forsyningsselskaber og anden infrastruktur i 28 stater, ifølge en AP-analyse.
En national klimavurdering udgivet af Det Hvide Hus sidste år bemærkede stigende hyppighed og intensitet af storme, efterhånden som klimaet ændrer sig. Det kan skubbe nogle dæmninger ud over, hvad de er designet til at håndtere.
Selvom det holdes i god stand, tusindvis af dæmninger kan være i fare på grund af ekstreme regnbyger, sagde Fugate, den tidligere FEMA embedsmand.
"Det er som tikkende bomber, der bare sidder der, venter på, at de forkerte forhold opstår for at forårsage katastrofalt svigt, " han sagde.
___

A vehicle passes over the spillway at Willett Pond on the border of Norwood and Walpole, Masse., 27. december, 2018. If the dam were to give way, it could send hundreds of millions of gallons of water into the heart of the Norwood, a Boston suburb of nearly 30, 000 mennesker. (AP Photo/Charles Krupa)
The nation's dams are categorized as high, significant or low hazard in the National Inventory of Dams database. High hazard means loss of human life is likely if a dam were to fail. A significant rating means no deaths are likely, although economic and environmental damage are possible.
There is no national standard for inspecting dams, leading to a patchwork of state regulations. Some states inspect high-hazard dams every year while others wait up to five years. Some states never inspect low-hazard dams—though even farm ponds can eventually pose a high hazard as housing developments encroach.
Dam conditions are supposed to be rated as unsatisfactory, poor, fair or satisfactory. But the ratings are subjective—varying by state and the interpretations of individual inspectors—and are not always publicly disclosed.
Since the Sept. 11, 2001, terror attacks, the U.S. government has cited national security grounds in refusing to include dams' conditions in its inventory, which was updated most recently in 2018. But the AP was able to determine both condition and hazard ratings for more than 25, 000 dams across the country through public records requests.
The tally includes some of the nation's most well-known dams, such as Hoover Dam along the Colorado River, but mostly involves privately owned dams. Many are used for recreation.
The AP then examined inspection reports for hundreds of high-hazard dams in poor or unsatisfactory condition. Those reports cited a variety of problems:leaks that can indicate a dam is failing internally; unrepaired erosion from past instances of overtopping; holes from burrowing animals; tree growth that can destabilize earthen dams; and spillways too small to handle a large flood. Some dams were so overgrown with vegetation that they couldn't be fully inspected.
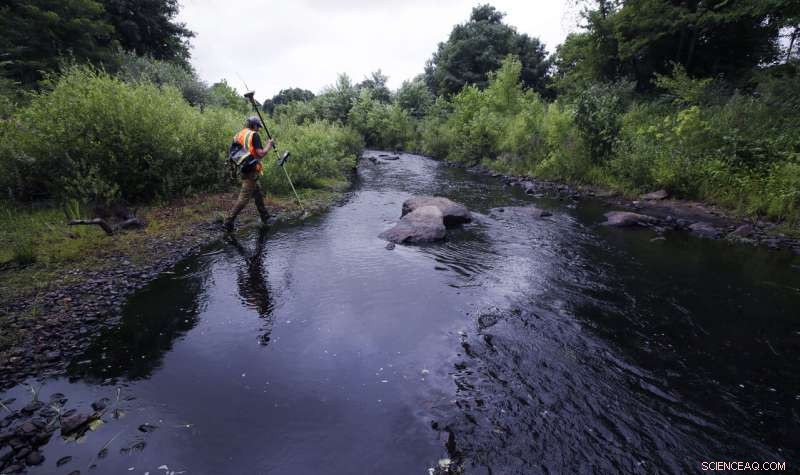

A surveyor walks the banks of the Mill River, at the site of the former Whittenton Pond Dam, just upstream from downtown Taunton, Masse., July 25, 2018. The dam was removed following concerns that the 170-year-old plus structure could fail, after it buckled and nearly failed in 2005. (AP Photo/Charles Krupa)
Georgia led the nation with nearly 200 high-hazard dams in unsatisfactory or poor condition, according to the AP's analysis.
Among them is Reservoir No. 1 in Atlanta, a 180 million-gallon water supply dating to the late 1800s that has been out of service much of the past few decades. The city made repairs and brought it back online in 2017, only to shut it down again after leaks were noticed.
If the dam were to catastrophically fail, the water could inundate more than 1, 000 hjem, dozens of businesses, a railroad and a portion of Interstate 75, according to an emergency action plan .
Joel Iverson has previously noticed water trickling out of the dam near the brewery he co-founded, Monday Night Brewing.
"If that one goes, it's going to wash away us and a lot of beer, " Iverson said.
The Atlanta Watershed Management Department declined the AP's request for an interview about the reservoir and instead asked for questions in writing. When those were submitted, it declined to answer them.
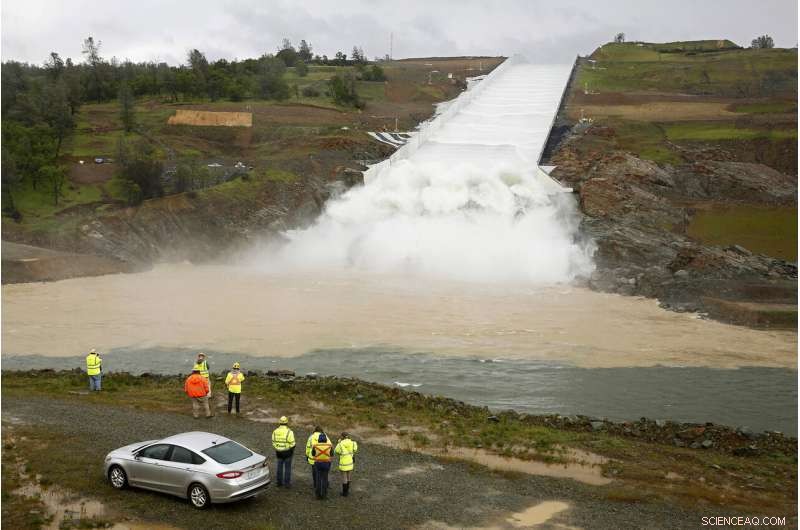

In this April 2, 2019, fil foto, water flows down the Oroville Dam spillway in Oroville, Calif. The state spent $1.1 billion repairing the Lake Oroville spillway, enacted new emergency plan requirements and launched a review of 93 other dams with similar spillways. (AP Photo/Rich Pedroncelli, Fil)
___
One of the most common problems for aging dams are spillways incapable of handling an extreme rainfall event.
If water can't escape quickly enough through spillways, it could flow over the top of a dam, which increases the probability of rapid erosion that can cause it to collapse.
The spillway at the 107-year-old Willett Pond Dam near the Boston suburb of Norwood is capable of handling just 13% of the water flow from a serious flood before the dam is overtopped, according to a recent state inspection report. If the dam were to give way, it could send hundreds of millions of gallons of water into the heart of the city of nearly 30, 000 mennesker.
"We are not talking of just flooding someone's house. We are talking about covering their house, " said Murray Beach, who lives on the shore of the 220-acre privately owned lake and belongs to a citizens group that has lobbied for years for the spillway to be repaired.
A 2017 inspection report said improvements to the spillway could cost between $1 million and $5 million. A nonprofit that owns the lake received a $215, 000 state grant last year to design spillway improvements. But there is no timeline to fix it.
I denne 30. nov. 2017, fil foto, work continues on the Oroville Dam spillway in Oroville, Calif. The scare at Oroville, the nation's tallest dam, led to evacuation orders for nearly 200, 000 mennesker, although no one was injured and the dam ultimately held. (AP Photo/Rich Pedroncelli, Fil)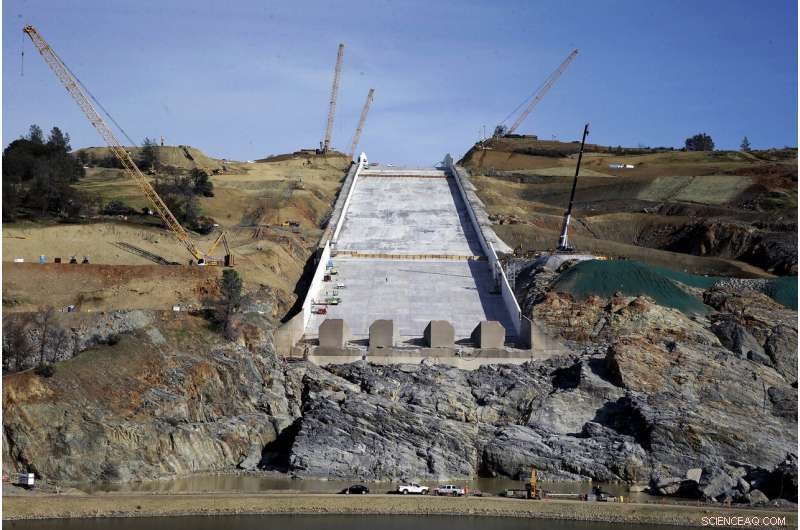 
Tamiko Porter, who operates a Montessori school serving some 75 students, said she was surprised to learn there was a dam upstream that could flood her school if it failed.
"Oh God, please let it happen when my kids aren't here, " sagde Porter.
Norwood emergency management director Bernard Cooper said there is no imminent risk of dam failure.
"Ja, it needs work. The spillway should be rebuilt. Absolutely, no question, " Cooper acknowledged. But "there is no money in the system for that."
Concerns about inadequate dam spillways date back decades to when the Corps of Engineers undertook its first nationwide assessment of dams posing a high risk to life and property. From 1978 to 1981, the Corps inspected 8, 818 dams. About one-third were deemed unsafe due to deficiencies, and about 80% of those cited inadequate spillway capacities.
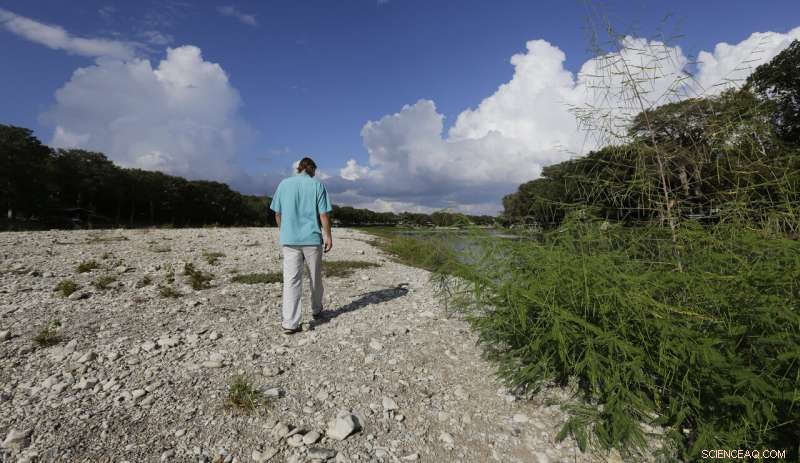

Hunter Croan walks along a dried-up section of Lake Dunlap, 30. september, 2019, in Lake Dunlap, Texas. Croan is one of many homeowners who were left high and dry, their lakeside docks now dry as the Guadalupe River retreated to its natural bed after the the center spill gate of the lake's 91-year-old dam failed. (AP Photo/Eric Gay)
One of the dams cited for a "seriously inadequate" spillway in 1978 was Lake Sebago, located in a New York state park near the village of Sloatsburg. Forty years later, nothing has changed.
A 2018 state inspection letter warned of "inadequate spillway capacity and dam stability" and asked for an improvement plan within 30 days. None was provided.
The state dam safety office has no authority to force the state parks department to make repairs.
To modify the Lake Sebago spillway, workers would have to rebuild a road and bridge that pass over the dam. The project could cost over $15 million, said Jim Hall, the recently retired executive director of the Palisades Interstate Park Commission, which manages multiple dams.
"That structure has been in place with the same spillway capacity for over probably 60 to 70 years and it hasn't been overtopped, " Hall said. "Should it be improved to meet all codes? Yeah, that would be nice. Does it make it the highest priority for us to do in relation to other dam structures we have? Probably not."
___
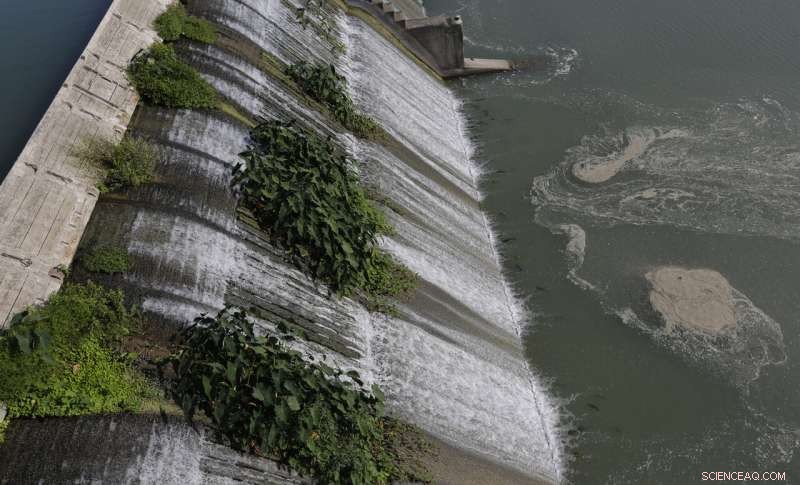

Water flows over a spill gate on Lake McQueeney, 2. okt. 2019, Lake McQueeney, Texas. A judge has issued a 12-month temporary injunction preventing the draining of McQueeney and five other lakes along the Guadalupe River after property owners sued. (AP Photo/Eric Gay)
In a 1982 report summarizing its nationwide dam assessment, the Corps of Engineers said most dam owners were unwilling to modify, repair or maintain the structures, and most states were unwilling to spend enough money for an effective dam safety program.
Siden da, every state but Alabama has created a dam safety program.
But the Great Recession a decade ago forced many states to make widespread budget and personnel cuts. Since a low point in 2011, states' total spending on dam safety has grown by about one-third to nearly $59 million in the 2019 fiscal year while staffing levels have risen by about one-fifth, according to data collected by the Corps of Engineers.
Californien, which runs the nation's largest dam safety program, accounts for much of that gain. It boosted its budget from $13 million to $20 million and the number of full-time staff from 63 to 77 following the failure of the Oroville dam spillway in 2017.
The scare at Oroville, the nation's tallest dam, led to evacuation orders for nearly 200, 000 mennesker, although no one was injured and the dam ultimately held. An independent investigation cited "a long-term systemic failure " by regulators and the dam industry to recognize and address warning signs.
California spent $1.1 billion repairing the Lake Oroville spillway, enacted new emergency plan requirements and launched a review of 93 other dams with similar spillways.
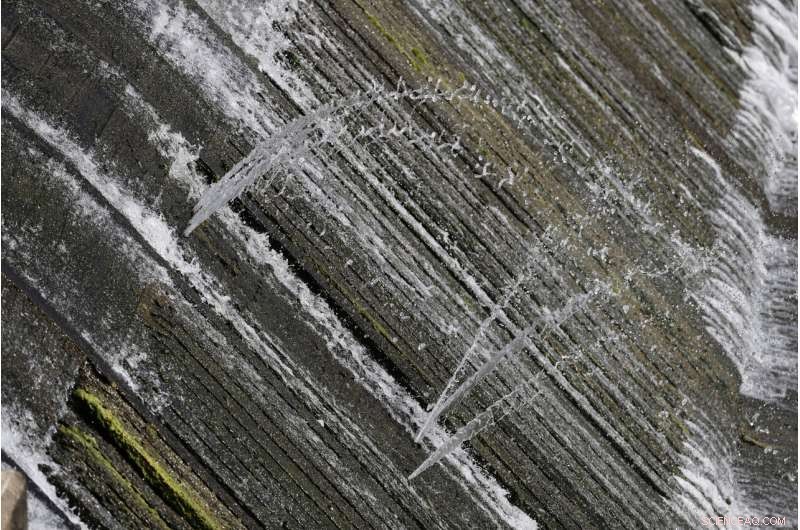

Water spurts through a wood section of a spill gate on Lake McQueeney, 2. okt. 2019, Lake McQueeney, Texas. A judge has issued a temporary injunction preventing the draining of the lakes along the Guadalupe River as a result of an agreement between suing property owners and the Guadalupe-Blanco River Authority. (AP Photo/Eric Gay)
I South Carolina, after more than 70 dams failed following heavy rains in 2015 and 2016, the state tripled the personnel in its dam safety program and ratcheted up spending from about $260, 000 annually to more than $1 million.
But some states have continued to pare back their dam safety programs. Thirteen states and Puerto Rico were spending less in 2019 than they did in 2011, and 11 states had fewer full-time positions in their programs.
The Association of State Dam Safety Officials says almost every state faces a serious need to pump additional money and manpower into dam safety programs.
"If you don't have the staff to inspect a dam, or don't have the authority to do that, you don't know what the problems are, " said the association's Ogden.
"If you are able to do the inspection but you can't follow up, and you have dam owners who don't have the resources to fix their dam, then ultimately you know what the problem is but you can't get it addressed, " han tilføjede.
Many states face a quandary when it comes to problematic private dams when they can't identify the owners. Rhode Island's two-person dam safety office last year listed 32 high- or significant-hazard dams with safety concerns whose owners were unknown.
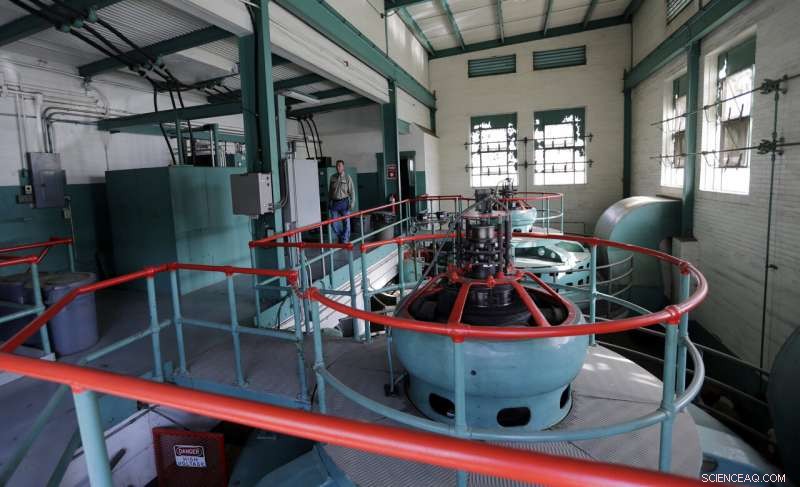

Guadalupe-Blanco River Authority's John Moryl walks through the hydroelectric plant at the spill gates on Lake McQueeney, 2. okt. 2019, in Lake McQueeney, Texas. The Guadalupe-Blanco River Authority announced plans to drain a chain of six lakes, including Lake McQueeney. (AP Photo/Eric Gay)
"If we don't know the owner, then we can't take any action to order anybody to fix it, " said David Chopy, chief of compliance and inspection for the Rhode Island Department of Environmental Management.
In some states, dams go uninspected because of exemptions in state law.
A 2013 Texas law exempts all dams on private property with a capacity of less than 163 million gallons that are rated significant or low hazard and are located outside of city limits in any county with fewer than 350, 000 mennesker. Som resultat, about 45% of its roughly 7, 200 dams are exempt from regulation.
Missouri performs safety inspections on only about 650 of its more than 5, 000 dams. That's because state law exempts all dams that are under 35 feet, used for agricultural purposes or subject to federal regulation.
Former Missouri Gov. Matt Blunt attempted to significantly expand the number of dams under state supervision after the mountaintop Taum Sauk Reservoir collapsed in December 2005, injuring a state park superintendent's family. But the legislation failed after some rural landowners expressed concerns. Then the proposal quietly faded away as new officials took over.
"Maybe it's time to take a look at that again and make sure that our dams are safe, " said Missouri state Rep. Tim Remole, who now leads the House committee overseeing dam safety.
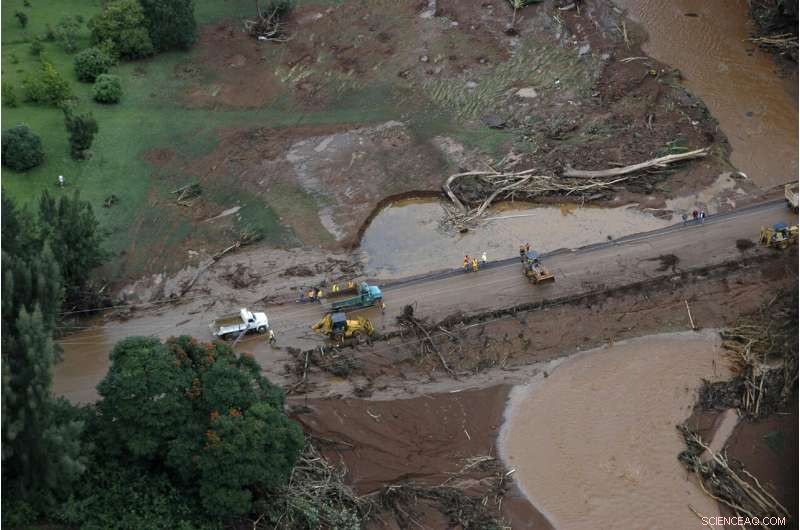

This March 14, 2006, fil foto, shows damage after a dam burst near Kilauea, on the Hawaiian island of Kauai. An earthen wall of the Kaloko Reservoir collapsed during heavy rains and sent a wave of water and mud rushing down a hillside. Seven people were killed on Bruce Fehring's property, including his daughter, son-in-law and grandson. (AP Photo/Casey Riemer, Fil)
___
Until Angel's death in Nebraska this year, the last fatal dam failure in the U.S. occurred on the Hawaiian island of Kauai in 2006.
An earthen wall of the Kaloko Reservoir collapsed during heavy rains and sent a wave of water rushing down a hillside. Seven people—including a pregnant woman—were killed on Bruce Fehring's property, including his daughter, son-in-law and grandson.
Fehring, who wasn't there at the time, got a phone call from a neighbor saying something terrible had happened. He was shocked by the scene.
"It took a while to register, and I went, 'Oh my God, everything's been washed away, '" Fehring recalled. "I mean, you have no idea the power of water (until) you see what it can do in a very short amount of time."
Dam owner James Pflueger pleaded no contest to felony reckless endangerment and was sentenced to seven months of confinement and five years of probation. His property company pleaded no contest to seven counts of manslaughter. Prosecutors said Pflueger had filled in the dam's spillway while attempting to make space for a waterfront development.
-
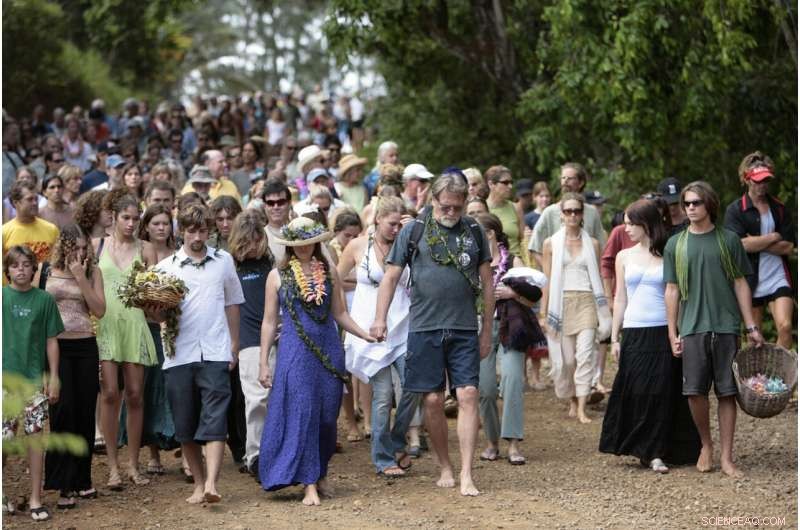

In this May 21, 2006, fil foto, Bruce Fehring and his wife Cyndee, centrum, lead a procession toward Kahili Quarry Beach during a memorial service to honor those killed when the Kaloko Dam failed in Kilauea, on the Hawaiian island of Kauai. An earthen wall of the Kaloko Reservoir collapsed during heavy rains and sent a wave of water and mud rushing down a hillside. Seven people were killed on Fehring's property, including his daughter, son-in-law and grandson. (Jamm Aquino/Honolulu Star-Bulletin via AP, Fil)
-
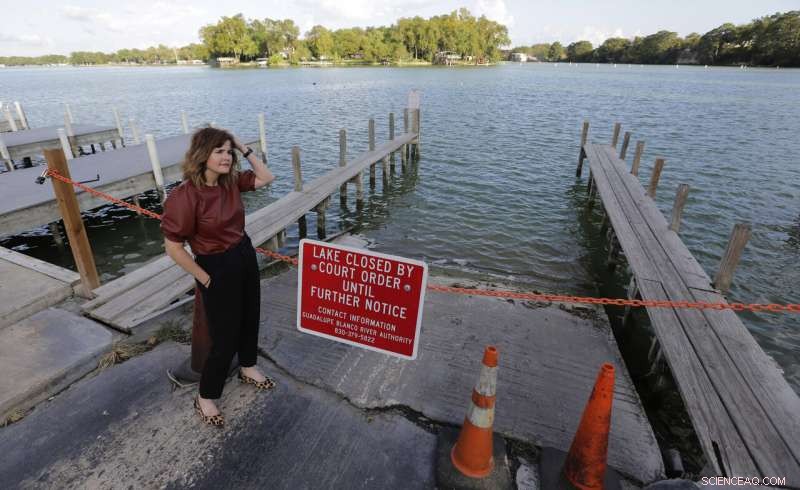

Tess Coody-Anders, a university executive and homeowner near Lake McQueeney, one of the dams slated to be drained, stands near a sign showing the lake is closed, 30. september, 2019, in Lake McQueeney, Texas. "This is something that communities and states all across the country are grappling with as we are reckoning with our aging infrastructure, " said Coody-Anders. (AP Photo/Eric Gay)
The victims' families and those whose property was damaged, including actress Bette Midler, agreed to a $25 million civil settlement. Though categorized by the state as low hazard at the time it failed, Kaloko Reservoir is now listed as a high-hazard facility in poor condition . It remains largely unrepaired.
That's also the case with Lake Dunlap Dam, northeast of San Antonio. On a sunny morning in May, one of the 91-year-old dam's corroded spillway gates suddenly gave way. No one was hurt in the rush of water, but scores of homeowners' lakeside docks were left high and dry, facing barren swaths of dried lakebed after the river retreated, leaving boats stranded.
The dam was the second hydroelectric facility along the river to fail within the past three years. The Guadalupe-Blanco River Authority responded with plans to drain a chain of four lakes because of concerns their similarly designed spillway gates also could fail.
But after property owners sued, the river authority agreed in September to a temporary injunction delaying the plan for a year. That could allow time to find funding for the estimated $90 million to $210 million to repair the dams.
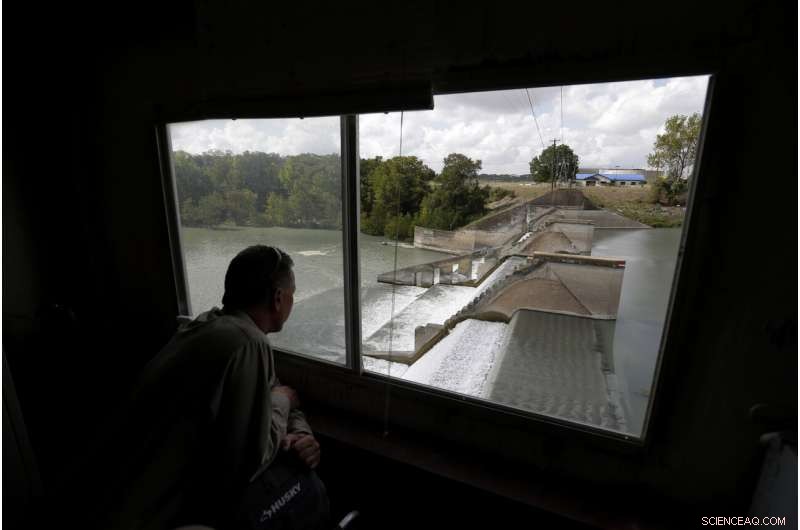

Guadalupe-Blanco River Authority's John Moryl looks over the spill gates at Lake Dunlap, 2. okt. 2019, in Lake Dunlap, Texas. One of the spill gates at the dam failed in May and the lake drained down to the original channel of the Guadalupe River. (AP Photo/Eric Gay)
"This is something that communities and states all across the country are grappling with as we are reckoning with our aging infrastructure, " said Tess Coody-Anders, a homeowner near Lake McQueeney, one of the dams slated to be drained.
"I hope that everyone will recognize that, like in our community, entire economies and ways of life have developed around what started out as a civil engineering project, " she added. "And you can't take that away."
© 2019 The Associated Press. Alle rettigheder forbeholdes.
 Varme artikler
Varme artikler
-
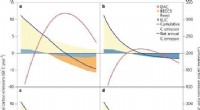 Tænk ud af boksen på klimabegrænsningFremskrivninger er baseret på et tærskeloverskridelsesbudget på 232 Gt C for 2015-2100, inklusive en RCP8.5 non-CO2 forcering23. Blå linjer viser årlige netto C-emissioner, røde streger er kumulative
Tænk ud af boksen på klimabegrænsningFremskrivninger er baseret på et tærskeloverskridelsesbudget på 232 Gt C for 2015-2100, inklusive en RCP8.5 non-CO2 forcering23. Blå linjer viser årlige netto C-emissioner, røde streger er kumulative -
 Gode nyheder og dårlige nyheder om skovfragmenteringLucy Hutyra og Andrew Reinmann fandt ud af, at New England -skove kan være mere følsomme over for klimaændringer end tidligere foreslået. Kredit:Cydney Scott I løbet af de sidste århundreder har s
Gode nyheder og dårlige nyheder om skovfragmenteringLucy Hutyra og Andrew Reinmann fandt ud af, at New England -skove kan være mere følsomme over for klimaændringer end tidligere foreslået. Kredit:Cydney Scott I løbet af de sidste århundreder har s -
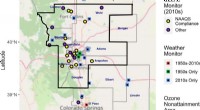 Høje temperaturer i Colorado på grund af klimaændringer udgør en stor sundhedsrisikoFig. 1:Undersøgelsesregion og monitoreringssteder. Studieregionen omfatter 17 amter, en i Wyoming og resten i Colorado. Den skitserede region er Metro Denver North Front Range ozon 2008 NAAQS nonattai
Høje temperaturer i Colorado på grund af klimaændringer udgør en stor sundhedsrisikoFig. 1:Undersøgelsesregion og monitoreringssteder. Studieregionen omfatter 17 amter, en i Wyoming og resten i Colorado. Den skitserede region er Metro Denver North Front Range ozon 2008 NAAQS nonattai -
 Hvorfor har planter og dyr brug for kvælstof?Kvælstof er et byggeblokelement både i atmosfæren, hvor det er den mest rigelige gas og i organismer. Dens strømning gennem jordens atmosfæriske, geologiske og biologiske systemer - kvælstofcyklussen
Hvorfor har planter og dyr brug for kvælstof?Kvælstof er et byggeblokelement både i atmosfæren, hvor det er den mest rigelige gas og i organismer. Dens strømning gennem jordens atmosfæriske, geologiske og biologiske systemer - kvælstofcyklussen
- Usynlighedens stråle
- United forsinker igen returneringen af Boeings 737 MAX
- Hvilke fælles stoffer absorberer mest energi fra solen?
- Nyopdaget Amazonas klippekunst viser regnskovenes tidligste indbyggere, der lever med gigantiske ist…
- Røntgenstråler gør proteinstrukturen større i hjertet af COVID-19-virus
- Californiens naturbrandfarer kan sprede sig mod syd