Hvordan de superrige erobrede London

Kredit:ZGPhotography/Shutterstock.com
Over kopper te i hans faldefærdige hjem i London chattede jeg med en romanforfatter. Det føltes som en værdifuld mulighed, givet hans mange fiktive behandlinger af London, for at diskutere byens hurtige forandringer, som jeg også skrev om.
Talen vendte uundgåeligt til dens voksende befolkning af velhavende indbyggere. Han fortalte mig, at han engang havde tænkt på at skrive en roman om de superrige, men konkluderede, at det i sidste ende ville blive for kedeligt. Hvad kan man sige om mennesker, hvis liv ikke var forbundet med andre? Hvad ville karaktererne blive vist at gøre med deres ubegrænsede tid?
I 1950'erne, den anerkendte sociolog C Wright Mills bemærkede, at ideen om, at eliten besatte en "trist, tomrum på toppen af samfundet" var, på mange måder, simpelthen en måde at blive forsonet med, at vi ikke er rige. Skuespilleren Michael Caine syntes senere at omarbejde Mills' udtalelse, da han kommenterede, at "tanken om, at penge ikke køber dig lykke, er en løgn, som de rige har fremsat for at forhindre de fattige i at dræbe dem".
I dag, ideen om en misundelsespolitik i Storbritannien ser ud til at tjene stort set samme formål – forslag om skattereformer og større bidrag bliver mødt med foragt – ofte med henvisning til ambitionernes kvælning, afskrækker skabelse af velstand eller, værst af alt, de rige flytter andre steder hen.
I min forskning om London er jeg kommet til at indse, at et af de allersidste steder, de rige ville forlade, er denne fine by. I virkeligheden, de rige har brug for byen som en astronaut har brug for en rumdragt:den giver et klimakontrolleret sted med komfort og støtte, uden hvilket deres liv ville være umuligt.
Byen er hjemsted for omkring 100 milliardærer og 5, 000 vi kan tænke på som superrige (dem med £20 millioner plus i ikke-boliger, disponible aktiver). Yderligere 350, 000 tæller som byens mere rige rige i mellemklassen (med omkring 700 £, 000 eller mere i aktiver).
Lige nu, midt i COVID-19-krisen, det er svært at huske, at vi for blot et par måneder siden fik at vide af formueanalytikere, at vi gik ind i en ny brølende 20'er. Men i modsætning til det årti med rigdom for et århundrede siden, denne ser ud til at starte med en Groundhog Day-gentagelse af den sidste krise i 2008 – med store spørgsmålstegn hængende over, hvordan man finansierer et økonomisk opsving, udsigten til udbredte ofre for virussen og en vedvarende recession i fremtiden.

Kig op. Kredit:silvester.alan@gmail.com, Forfatter oplyst
Formuerne for verdens 20 rigeste er blevet barberet af omkring 293 milliarder USD i de seneste tre måneder. Blot et par dage senere fandt vi ud af, at andre milliardærers formuer var vokset betydeligt. Den generelle regel, på trods af de enkelte riges skiftende formuer, er, at penge fortsætter med at regne opad.
Så det ser ud til at være klart, at de med rigeligt vil mere end overleve den økonomiske krise, der er genereret af COVID-19. På samme måde kan vi se, at Londons position som alfaby sandsynligvis ikke vil blive påvirket, selv af truslen om pandemi og recession. Dets regeringssystemer, virksomhedsliv og økonomi er mere robuste og effektive, end vi måske tror.
Kig op
Jeg har af og til talt med forskere, som bl. når de diskuterer deres arbejde på de rige eller magtfulde, imødekomme responsen om, at det, de studerer, er spild af tid og kræfter. Jeg husker stadig kommentaren fra et byrådsmedlem, som da jeg begejstret sagde, at jeg arbejdede på Londons rige, spurgte blidt:"Hvorfor ikke noget om Sheffields stakkels?" Av.
Alligevel er det kritisk at undersøge elitens og de riges liv og virkning. En del af årsagen til dette ligger bundet i de ofte usynlige forbindelser, som vi kan spore mellem rig og fattig, de udelukkede og dem, der ellers er skadet af de overdrevne uligheder i samfund globalt.
De velhavende er en beskyttet og problematisk flok. Efterhånden som regeringskontrakter uddeles til medlemmer og donorer af det britiske konservative parti, da der gives redningsaktioner til velhavende og profitable virksomheder, og som skatteunddragelse, hvidvaskning og bedrageri er identificeret i flere rapporter, vi ser de metoder, hvormed rigdomme udvides eller udskilles. Indflydelsesrige rapporter har også vist, at i tilfælde af jordbesiddelse (1 % af Storbritannien ejer 50 % af jorden), skattely, store penge og politisk indflydelse, wealth is a question that should interest everyone.
If we really want to understand the poverty and problems of many people we would do well to look up. In an unequal society, divisions focused around housing, beskæftigelse, material poverty, health and care can be traced back to economic and political decisions, and to the operation of societies that repeatedly produce the same winners and losers.
Fresh from my doctoral studies in London I landed as a green researcher in the world of opportunity that was Glasgow—the first Labour government in 18 years pumping investment and resources into poorer urban communities and employing social scientists to monitor these issues and consider how to resolve these problems. That seems an entirely different world to the one we inhabit today, on so many levels.
Since then the UK has had a massive financial crisis, years of public funding cuts, massive social distress, only to face these problems again in a more extreme form as COVID-19 wreaks havoc. And this pattern is mirrored in numerous other countries.

Glasgow:a world of opportunity. Credit:TreasureGalore/Shutterstock.com
I cut my teeth on studies of how households were displaced from gentrifying areas of the city. In Glasgow, I worked with colleagues on the question of how areas of concentrated poverty affected their residents. But I also remained interested in how the middle classes affected life in the city and turned back to study gentrification, and then gated communities in England.
One way of summing up this body of work lies in the idea that space is important to social relationships and a sense of togetherness—with new suburban extensions to cities and gated estates fuelling a kind of break in social relations that damages urban life in subtle ways. In the UK's cities the sense of social and physical distance was, in complex ways, changing, breaking down and remaking urban social life. Cities were proclaimed to be increasingly privatised, unhappy and divided in the 2000s. Worse, all of this had been happening even as they were targeted for improvement and investment.
While this situation was clearly not comparable to the hyper-segregated and often risky US metropolis, the UK's public history of open streetscapes and democratic urban centres was clearly being eroded. The market had been allowed to run freely as a means of boosting state expenditure and what was described as an urban renaissance more often appeared to produce inferior copies of Barcelona squares, with low-grade apartments and multiple signs telling us not to park.
And then the rich arrived.
The alpha city
I had dinner with one of London's elite real estate agents, an imposing figure, vital, well groomed, super-confident. He told me he could show me round some of the homes available locally, costing in some cases more than £10m, but I would need to undergo criminal checks first. Talk turned to why I am doing the study. Of course he is all for sociologists learning more about how the property market works, han sagde. But a look in his eye suggested sudden wariness.
London has always been a wealthy city, but it has seen a step-change in its fortunes in recent decades. Though right now the market is on ice and has seen the volume of sales decrease, it is still the case that numerous super-prime homes are sold each year. Many of these sales are to wealthy urban Brits but a substantial proportion, often much more than half in some neighbourhoods, go to offshore anonymous buyers through trusts, or to wealthy international investors and buyers.
You will be familiar with the story and rising criticism, that much of London's housing development has been a process of accommodating dollars, rather than people. Property becomes something to borrow against, buy and trade on an upward rising bubble of prices, fuelled by more speculation and borrowing, and the arrival of many more people from around the world with bundles of cash to spend. I mange tilfælde, such homes are bought and lie empty, or are used to store criminal cash as it is laundered or from huge reserves held offshore (around US$36 trillion). Today it is estimated that around 42, 000 properties in London have been purchased from these sources. These aspects of London's apparent success on the world stage give rise to the impression that it is a landscape of riches built on dodgy money, which has done little to contribute to the wider city, except to generate even further rises in house prices.
The elite agent I'd had dinner with later emailed me to say that it would, ved eftertanke, not be possible to do a tour of one of the local mansions. He wished me good luck with the research.

In the alphahood. Credit:silvester.alan@gmail.com, Forfatter oplyst
London is a receiver and maker of the global finance economy. Its resplendent position is derived from intertwining histories, of the industrial revolution, of fortunes made by old and new elites jostling for place in growing cities. It is a history that takes in empire, its subsequent fall and the eyeing of new opportunities in order to retain an economic, if not military, position on the global stage.
The City of London is critical to this series of changes and, with it, the political system has taken on and helped to broadcast the apparently commonsense view that what is good for this goose is good for the country more broadly. The City is linked to other golden egg-laying entities—numerous tax havens, flows of international capital and so on. Much of this goes on in a high trust, low regulation environment designed to capture this wealth and maintain a powerful homegrown industry on the back of it.
London's broader "offer", of fine homes, beautiful urban neighbourhoods often attached to parks, luxury services and shops, welcoming plush hotels and a sense of grandeur and place, cement the economic value of the city as a place to actually live and take a seat alongside the existing elite. As one walks these areas, small glimpses of the incredible niceness of life at the top can be gleaned:a sense of ease, comfort and confidence.
This world has been mothballed by COVID-19, but lockdown for the elite is not the same thing as for everyone else:with ample space and money, they suffer the least.
Wall of money
Walking over Charing Cross bridge one day last year I saw a wall of cranes standing above the Shell Centre. A report I was carrying in my bag told me that more than 90% of these apartments have been sold to anonymous offshore jurisdictions.
Drinking a coffee in the lobby of one of the city's newest five star hotels, the almost invisible but helpful staffer offered me a copy of The Times. I read about Zamira Hajiyeva, the banker's wife who spent £16m in Harrods over just a few years, and the long process by which the National Crime Agency came to the conclusion that her fortune was of dubious origin. Yet this case has remained among a mere handful targeted at those laundering illicit proceeds (and whatever happened to a report on Russian money in British politics?).
A property investor told me he knows that there are many thousands of these cases but that they will never see the light of day. Why should politicians and police forces become overly moral about crimes where the only seeming impact is to create a market in overpriced homes? I turned back to my copy of the Guardian and read that 130, 000 preventable deaths have been linked to austerity cuts to public services.
Money and investment capital is a force to be reckoned with. It propels the construction of high-rise blocks, carves out the ground beneath palatial homes by the thousands, created new super-prime residential blocks and delivered fortunes to those mediating these changes. JCBs are left entombed inside—perhaps as many as 1, 000 over the past two decades—not worth the cost of extracting them.

Mansions in London’s borough of Kensington. Credit:Nielskliim/Shutterstock.com
Yet each day I seem to read reports in the FT under which reader comments are either filled with disgust at who the city has been opened up for or, alternatively, confused at what is the fuss about—if we don't take their money, some other city surely will? Yet to suggest that the rich are an unadulterated gift to the city would be a mistake.
One way of thinking about what London has become is to describe it as an alpha city. This term denotes a pre-eminent position in the global capitalist world economic and political order. But we can also use it to offer a deeper idea about what the city has become—a grasping political and economic machine whose very culture is infused with the need to maintain its position via an open faucet of global capital because, godt, this will float all boats, ret?
You will know this argument, but you may not be fully aware of the rotten foundations on which it stands. The city works in concert with its property lobbyists and, via appeals to the need for development and unending rounds of global capital investment, to help ride out the risks of economic downturns and reverses. Come rain or shine, the city works hard to position itself as the preferred destination of many of the international super-rich. Endnu, simultaneously, this is a city where an estimated 200, 000 have lost their homes from the demolition of housing estates.
The city is a site of wealth creation, but also a place in which the areas in which the rich live—its alphahoods if you will—enable social and power networks to become established in both open and shadier ways. This is not because there is some grand, fraudulent practice at work among the city's elites. Instead there is an idea, a sense of how the city should work and what it can deliver, and this notion galvanises and animates many tens of thousands of people who work to ensure that it is protected—because their own pay cheques rely on it.
The idea of the alpha city resides in the sense that upward marching property values are a good thing, that the City of London is gift to city and country, that the rich are self-made wizards of finance, property and technology, and that the maelstrom of urban life that results from these various ingredients makes London simply the best city in the world.
But many of London's inhabitants are, i virkeligheden, victims of this idea. This includes many graduates, new operators of the banking system sharing a flat to get by and many other well-paid professionals who themselves struggle, or see their children floundering in an overpriced housing market.
I dag
Right here, lige nu, it doesn't seem possible to think of London as the keystone city in a finance system that bridges the world, a place in which the rich, honeyed capital and pampered bodies will again flow. At this very moment the city's cautiously refilling streets feel deflated by the COVID-19 crisis, like those of its similarly wealthy counterparts, Hong Kong and New York.
The city's frenetic activity, the wheeling, dealing and the snapping up of luxury homes and other trophy assets are temporarily on ice. Yet only a moment before the city went into lockdown a home was sold, the most expensive ever in the city, to a single Chinese buyer for more than £200 million. In just the first three months of 2019 £1.3bn of homes were sold in the city priced at more than £5 million, the price above which is broadly included as "prime" sales.

Do we want to go back to normal? Credit:Kid Circus/Unsplash, FAL
På trods af dette, many in the development and property sectors have complained of the impact of tax tweaks, the impact of Brexit and then a potential death blow dealt by COVID-19. All of this sets the scene for how we might imagine or hope the city to recover, a crossroads much like that after the 2008 financial crisis from which the social disaster of austerity was unleashed. Calls for tax cuts and help for the property sector are already evident.
Now there is something of a great stink. Men, unlike the infamous event in which the Thames became blocked following the cholera epidemic of 1848, today it is the fuss being made over wealth and its corrupting influence on the city. The rule of profit-maximising developers and compliant local authorities will continue unless stronger challenges are mounted – planning will need to be reworked and social housing should see a resurgence through state investments (these could be plugged into a green new deal that could prop up builders seeing hard times).
The furious debates to come will also be fuelled by anger over inequalities that were made more transparent by COVID-19. The treatment of key workers in health and social care is one sign of an apparent groundswell of demands for greater recognition of those who are not part of the alpha economy, its losers who are clearly so precious. Commitment to social justice all too easily wavers. One minute the street homeless problem was, as if by magic resolved as the government funded a scheme to bring the homeless off the streetsduring the COVID-19 crisis. A moment later this funding was withdrawn, and rough sleepers are soon to emerge blinking and back on the streets.
It seems possible that future debates about how we plan, build and manage a city like London will be influenced by these inequalities as the roadmap to recovery is slowly unfolded. We should likely be much more angry than we are already, but this ire should be positively channelled toward whatever opportunity we get to make a better choice to ensure London and all of our cities and communities see a more sustainable and socially just future.
At være sikker, it is a nice life, existing inside the warm circuits of the alpha city. Emerging after a week's fieldwork into a less salubrious part of town I felt a strange sense of risk and disorderliness that I had not recognised before. Arriving back in my university city, getting the tram home, I passed the bodies and faces of those marked by poverty and a kind of anger arose in me as I realised how entirely avoidable and invisible these lives were to those living in London's rich neighbourhoods.
This point belies a much deeper issue. What does poverty mean to the owner of an opulent penthouse on the Thames, a luxury home in a gated community or a palace built from tech wealth in Mayfair? How can the demands of those who are rewarded so little be made to be heard and to generate traction for even modest commitments to contribute more by the well-off. None of this is to suggest that the rich are in some way ignorant or unaware of what it means to have little, and many of them care a great deal. But this does not detract from the powerful role of money and place in adding vitality to popular ideas that wealth is justified and that the poor can be vilified or ignored.
På mange måder, we may hope that London becomes a "beta" city, to the benefit of all its citizens.
Denne artikel er genudgivet fra The Conversation under en Creative Commons -licens. Læs den originale artikel. 
Sidste artikelVil biografer overleve COVID-19?
Næste artikelVideo:De lange arme og korte ben krige i palæoantropologi
 Varme artikler
Varme artikler
-
 Napoleonske juveler blænder i Genève-auktionennapoleon Et smykkesæt båret af den franske kejser Napoleon Bonapartes adoptivdatter blev onsdag solgt for 1,65 millioner dollars i Genève. svævende langt over skønnet før auktionen. I anledning a
Napoleonske juveler blænder i Genève-auktionennapoleon Et smykkesæt båret af den franske kejser Napoleon Bonapartes adoptivdatter blev onsdag solgt for 1,65 millioner dollars i Genève. svævende langt over skønnet før auktionen. I anledning a -
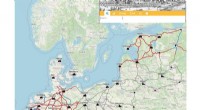 Afsløring af hansetidens ruter onlineBillede, der viser området dækket af Viabundus digitale kort. Forskere har bygget en digital platform, der afslører langdistancehandelsruter i Nordeuropa mellem 1350 og 1650. Kredit:viabundus.eu H
Afsløring af hansetidens ruter onlineBillede, der viser området dækket af Viabundus digitale kort. Forskere har bygget en digital platform, der afslører langdistancehandelsruter i Nordeuropa mellem 1350 og 1650. Kredit:viabundus.eu H -
 10 uidentificerede lyde, som forskere ser seriøst ind påVi lever i en verden mættet af støj. Men nogle af lydene er forvirrende. evgenyatamanenko/iStofck/Thinkstock Vi mennesker er ret gode til at genkende lyde. Vores ører er tilstrækkeligt følsomme til,
10 uidentificerede lyde, som forskere ser seriøst ind påVi lever i en verden mættet af støj. Men nogle af lydene er forvirrende. evgenyatamanenko/iStofck/Thinkstock Vi mennesker er ret gode til at genkende lyde. Vores ører er tilstrækkeligt følsomme til, -
 At finde modstandsdygtighed i lokale, samfundsnyhedsindsamlingKredit:CC0 Public Domain Når Webster-Kirkwood Times , en samfundsavis i det større St. Louis, Missouri område, måtte udstå fyringer og stoppe med at udgive sin trykte udgave - på grund af et tab
At finde modstandsdygtighed i lokale, samfundsnyhedsindsamlingKredit:CC0 Public Domain Når Webster-Kirkwood Times , en samfundsavis i det større St. Louis, Missouri område, måtte udstå fyringer og stoppe med at udgive sin trykte udgave - på grund af et tab
- Udvikling af værktøjer til klimabevidste investeringer
- Stabilisering af borafluorenanionen med carbener
- Billede:Farverne i Saturns ringe
- CryoSat erobrer is på arktiske søer
- Supercomputer hjælper forskere med at finde nye funktioner, mekanismer i tornadoer
- Indlandsisen smelter:skøn stadig usikre, eksperter advarer